Shodan is a search engine that exposes vulnerabilities of different kinds of operating systems and hardware devices. Shodan can also enable users to search an Internet of Things (IoT) by searching the network created by the devices connected to the internet and gather information like the operating system being used or a service that is running on a specific port. Shodan uses banner grabbing to gather information. Banner grabbing is the act of getting software banner information (name and version), whether it's done manually, or by using any OSINT tools that can do it for you automatically.
![Introduction to Shodan Search Engine [Ethical Hacking Tutorial]](https://www.socialyzehub.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/shodanse.jpg)
Introduction to Shodan Search Engine [Ethical Hacking Tutorial]
Also Read: What is a Reverse Shell [Ethical Hacking Tutorial]
The basic unit of data that Shodan gathers is the banner. The banner is textual information that describes a service on a device. For web servers this would be the headers that are returned or for Telnet it would be the login screen.
Shodan can also scan ports in a network especially that are mostly used and known ports running commonly used services like SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet, FTP, and devices like router, printers, CCTV cameras, Network devices, Webcam.
NOTE:
Crawlers
The Shodan crawlers operate around-the-clock and continuously update the database. They can scan the entire country's network from anywhere in the world. When you search the Shodan website, you always get the most recent view of the Internet. The distribution of Shodan Crawlers across numerous nations ensures that data collection will not be impacted by any kind of national blocking. The basic algorithm for the crawlers is:-
1. Generate a random IPv4 address.
2. Generate a random port to test from the list of ports that Shodan understands.
3. Check the random IPv4 address on the random port and grab a banner.
4. Go to 1
The crawlers do not scan incremental network ranges as a result. To guarantee uniform Internet coverage and avoid bias in the data at any given time, the crawling is conducted at random. The crawlers look for clues as to what web technologies were employed in the development of a website. The HTML and headers for the http and https modules are examined to identify the different parts of website.
Types of Interface
Shodan is provided with two kinds of Interface that we can use:-
- Web Interface, and
- Command Line Interface.
Web Interface
It is the easiest way to use Shodan to access data that it gathers from all over the world. We will see some of the web interface components below.
Shodan Search Query
The search query doesn't typically look at the meta-data; it merely scans the main banner text by default. For instance, if you search for "Google", the results will only contain websites where the word "Google" appeared in the banner; Google's network range may not necessarily be returned.
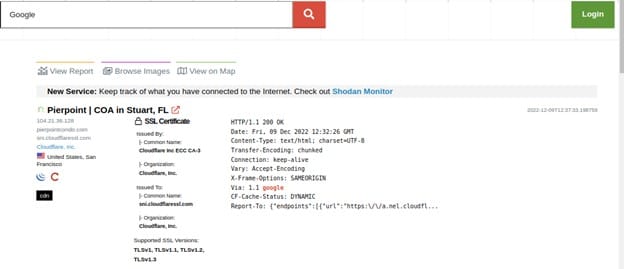
The Shodan Search Query has a search term filter. Shodan employs filters, which are specific keywords, to let you limit search results based on a service or device's meta-data. We can use the following format to filter our search query:-
Filter name: Value
For example we can search for a country by typing:-
City: “Addis Ababa”
Port: 443, 23, 8080. 8888
The search query will by default look at information gathered within the last 30 days. This differs from the previous website at shodanhq.com, which by default searched the whole Shodan database. This indicates that the website's results are up-to-date and accurately reflect the state of the Internet right now.
After completing a search there will be a button at the top called Download Data. Clicking on that button will provide you with the option of downloading the search results in JSON, CSV or XML formats.
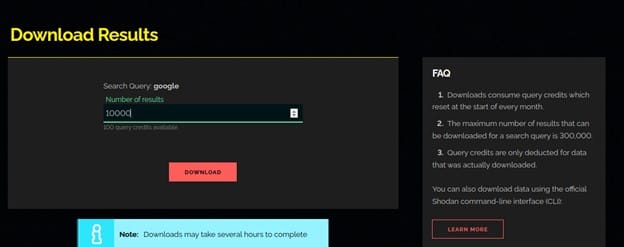
Generate Report
The website lets you generate a report based off of a search query. The report contains graphs/ charts providing you a big picture view of how the results are distributed across the Internet. This feature is free and available to anyone.
When you prepare a report, Shodan is tasked with gathering an overall picture of the search results and providing it to you in a snapshot form. As fresh data is gathered by Shodan, the report does not alter or automatically update once it has been prepared.
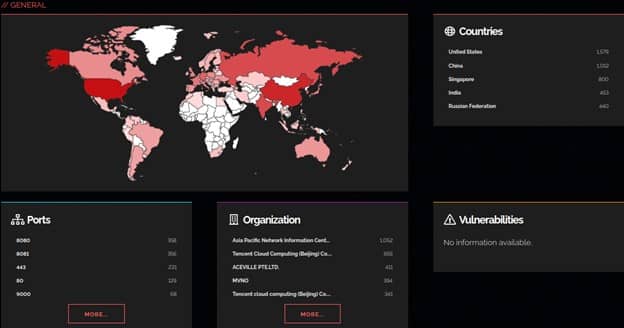
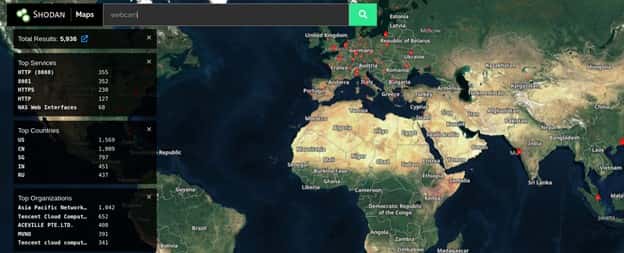
Shodan Map
Instead of using the main website's text-based search results, Shodan Maps offers a visual approach to explore search results. When you zoom in or out, Maps adapts the search query to only show results for the area you're looking at. It can display up to 1,000 results at once.
Shodan Exploits
Exploits default to searching the whole accessible exploit's content. data that includes meta-data. Contrary to Shodan, which only looks through banner text if no additional filters are set.

The following search filters are available:-
Name Description
Author Author of the vulnerability/ exploit
Description Description
Platform Platform that it targets (ex: php, windows, linux)
Type Exploit type (ex: remote, dos)
Shodan Images
For a quick way to browse all the screenshots that Shodan collects check out Shodan Images. It is a user-friendly interface around the has_screenshot filter.
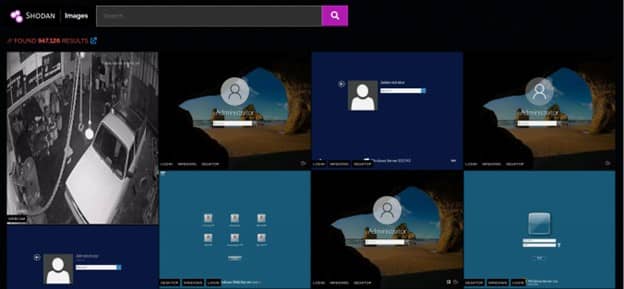
The search box at the top uses the same syntax as the main Shodan search engine. It is most useful to use the search box to filter by organization or netblock. However, it can also be used to filter the types of images that are shown.
Command Line Interface
The shodan command-line interface is packaged with the official Python library for Shodan, which means if you’re running the latest version of the library you already have access to the CLI. To install the new tool simply execute below command.
$ pip install shodan #or
$ easy_install shodan
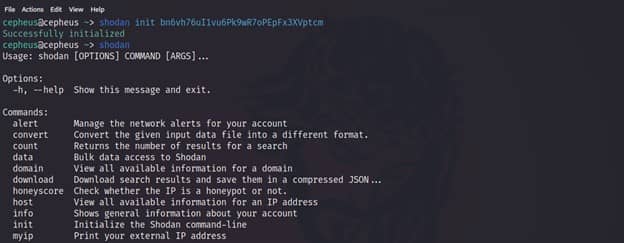
Once we have shodan installed, we can initialize the process by entering below command:-
$ shodan init API_KEY
We can get the api key from the Web interface. Shodan will provide an API_KEY for each user in order them to use.
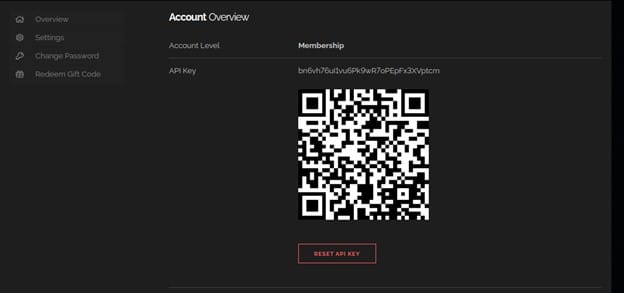
We will copy the api key and paste it to our terminal and hit Enter.
Download with Shodan CLI
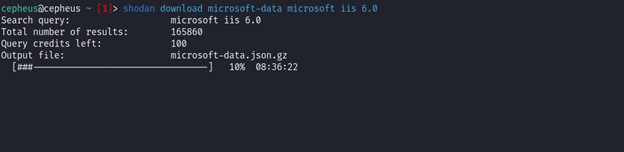
The download command is what you should be using most often when getting results from Shodan since it lets you save the results and process them afterwards using the parse command. Because paging through results uses query credits, it makes sense to always store searches that you’re doing so you won’t need to use query credits for a search you already did in the past.
Searching Targets with Shodan CLI
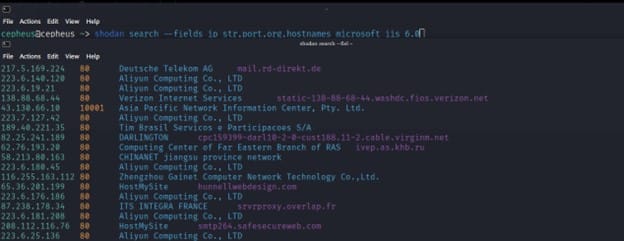
This command lets you search Shodan and view the results in a terminal-friendly way. By default it will display the IP, port, hostnames and data. For example, to search Microsoft IIS 6.0 and print out their IP, port, organization and hostnames use the following command:-
$ shodan search --fields ip_str,port,org,hostnames microsoft iis 6.0
Conclusion
Shodan allows users to find out what devices are now online, where those devices are located, and who is using them. Almost any system, including business networks, security cameras, industrial control systems (ICS), and smart homes, could contain such devices. Shodan, which indexes information based on banner content metadata that servers transmit back to hosting clients - can be utilized similarly to Google. Shodan searches should be run utilizing a set of filters in a string format for the best outcomes.
